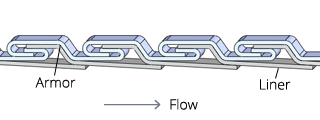
Care should be taken when specifying a stripwound hose assembly. Each of the components can have a dramatic effect on the assembly’s performance. In addition to carefully selecting components, the way they are assembled is also very important. Hose Master has developed fabrication techniques that help maximize the assembly’s performance. Two of these techniques are square cutting the hose ends and welding on the inside of the fittings.

The stripwound profile is helical. When it is cut by traditional methods, the hose end will also be helical. This creates a gap between the fitting and the end of the hose. This gap can cause the fittings to separate from the hose during use. Square cutting ensures that the hose end and the fitting are flush, leaving no gaps.
If the fittings are welded on the hose, welding the inside provides for a smooth transition between hose and fittings, preventing product from becoming damaged.
Specifying a Stripwound Hose Assembly:
Designing a stripwound hose assembly requires the determination of five factors:
- Hose (type, alloy, and size)
- End fittings (type, alloy, and size for each end)
- Assembly length
- Fabrication options
- Accessories
If these factors have been determined, a fabricator will be able to make the assembly. If not, these questions may be answered by proceeding to the next section.
Analyzing an Application:
To properly design a metal hose assembly for a particular application, the following design parameters must be determined. To help remember them, they have been arranged to form the acronym “S.T.A.M.P.E.D.”
- Size – The diameter of the connections in which the assembly will be installed is needed to provide a proper fit. This information is required.
- Temperature – As the temperature to which the assembly is exposed (internally and externally) increases, the strength of the assembly’s components decreases. If you do not provide this information it will be assumed that the temperatures are 70 deg F.
- Application – This refers to the configuration in which the assembly is installed. This includes the dimensions into which the assembly must fit as well as the details of any movement that the assembly will experience. This is required since you cannot determine the proper length or proper hose type without it.
- Media – Identify all chemicals to which the assembly will be exposed, both internally and externally. This is important since you must be sure that the assembly’s components are chemically compatible with the media. If no media is given, it will be assumed that both the media and environment are compatible with all of the available materials for each component.
- Pressure – Identify the internal pressure to which the assembly will be exposed. Stripwound metal hose, by the nature of its construction, is not pressure tight. However, pressure and media infiltration through the stripwound wall can be minimized by the insertion of one of a variety of packings into the wall during hose manufacturing. If no pressure is given it will be assumed that there is no pressure.
- End Fittings – Identify the necessary fittings. This is required since fittings for the assembly must be chosen to properly fit the mating connections.
- Dynamics – Identify the velocity at which the media will flow through the assembly. Extremely high flow or abrasive media can cause premature failure. If no velocity is given, it will be assumed that the velocity is not fast enough to affect the assembly’s performance.